Very basically speaking, recrystallization temperature is the point at which a metal becomes sufficiently ductile to be shaped without breaking. Ductility is the measure of a material’s capacity to be shaped without breaking. Generally, the higher the temperature to which a metal is heated, the higher its ductility. Read More…
At Grand Steel Products, Inc., we are a leading provider of steel service center solutions, offering a comprehensive range of products and services to meet the diverse needs of our clients. With years of experience and a commitment to excellence, we have established ourselves as a trusted partner in the steel industry, delivering reliable solutions that optimize supply chain efficiency and meet...

The Steel Supply Company brings you alloy, carbon and stainless steel shafting and tubing. Our steel fabrication services include hard chrome plating, induction hardening, honing, grinding, and non-standard items in order to meet your specifications. Visit our website to see our product line of both bars and tubes. We are ISO 9001:2008 certified.

As product specialists, we can meet your stainless steel needs. We stock T304304- and T303-grade stainless steel, as well as other cold-finished carbon bars. Pennsylvania Steel provides cold finished bar, tool steel, aluminum, stainless steel, tube/pipe, hot rolled bar, sheet/plate, expanded metal & grating, copper, brass and bronze. Visit soon!
As a world-class source for steel products, King Steel Corporation supplies companies across North America with what they need to get the job done. For over 50 years, we have continued to invest a great amount of both time and capital into purchasing new equipment and streamlining our processes. We’ve worked diligently to develop and maintain a reputation in our industry that represents growth, ...
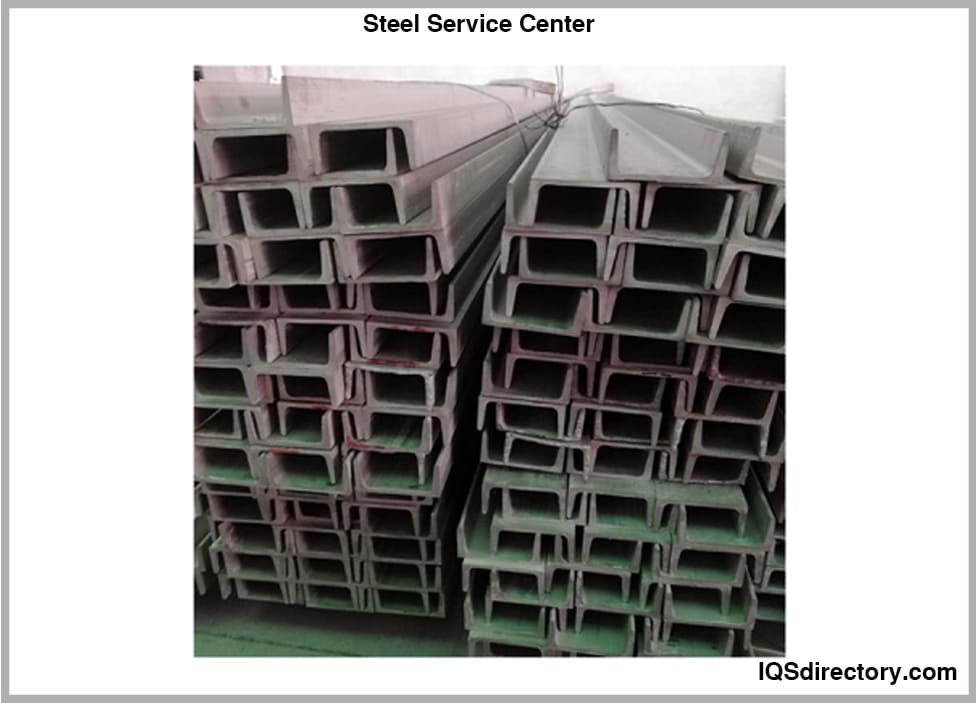
More Hot Rolled Steel Service Centers
When steel is heated beyond its recrystallization temperature and pushed between a set of rollers, the sheets that emerge from the rolling process exhibit qualities of high strength and good formability. This type of steel is not as hard as cold rolled steel, but is often used for high strength and structural applications within the automotive, appliance, railroad and ship building industries.
Hot rolled steel is used for a wide variety of products, such as frame components for cars, wheels, tubing, agricultural equipment parts and machinery parts. It is usually a blue-grey color and is only painted if it has been pickled with zinc or iron phosphates. This type of steel is available in yield strengths up to 60 ksi.
To produce hot rolled steel, steel service centers heat semi-finished slabs of steel nearly to their melting point in a furnace, where they become easily moldable. The slab is pushed through a set of rollers, a process comparable to rolling cookie dough with a rolling pin. Its thickness is cut down from eight or nine inches to between one and 1.5 inches.
The steel is then cropped into different shapes by a pair of steel drums with large shearing blades and left to return to room temperature. As it cools, a metallurgical transformation in the steel's crystal structure takes places, which hardens the steel considerably. Outside processing, such as pickling, temper rolling, re-squaring, slitting and cutting-to-length is done after the rolling process is complete.
Pickling, for example, is the process of surface treating hot rolled steel with strong acids. Because steel is susceptible to oxidization, especially when exposed to heat, hot rolling can cause an undesirable film to form on the surface of the steel. Pickling can remove this film without risking deformation to the steel's surface. Other physical machining processes can also be used to remove such films.







 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers Aluminum
Aluminum Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze Magnets
Magnets Nickel
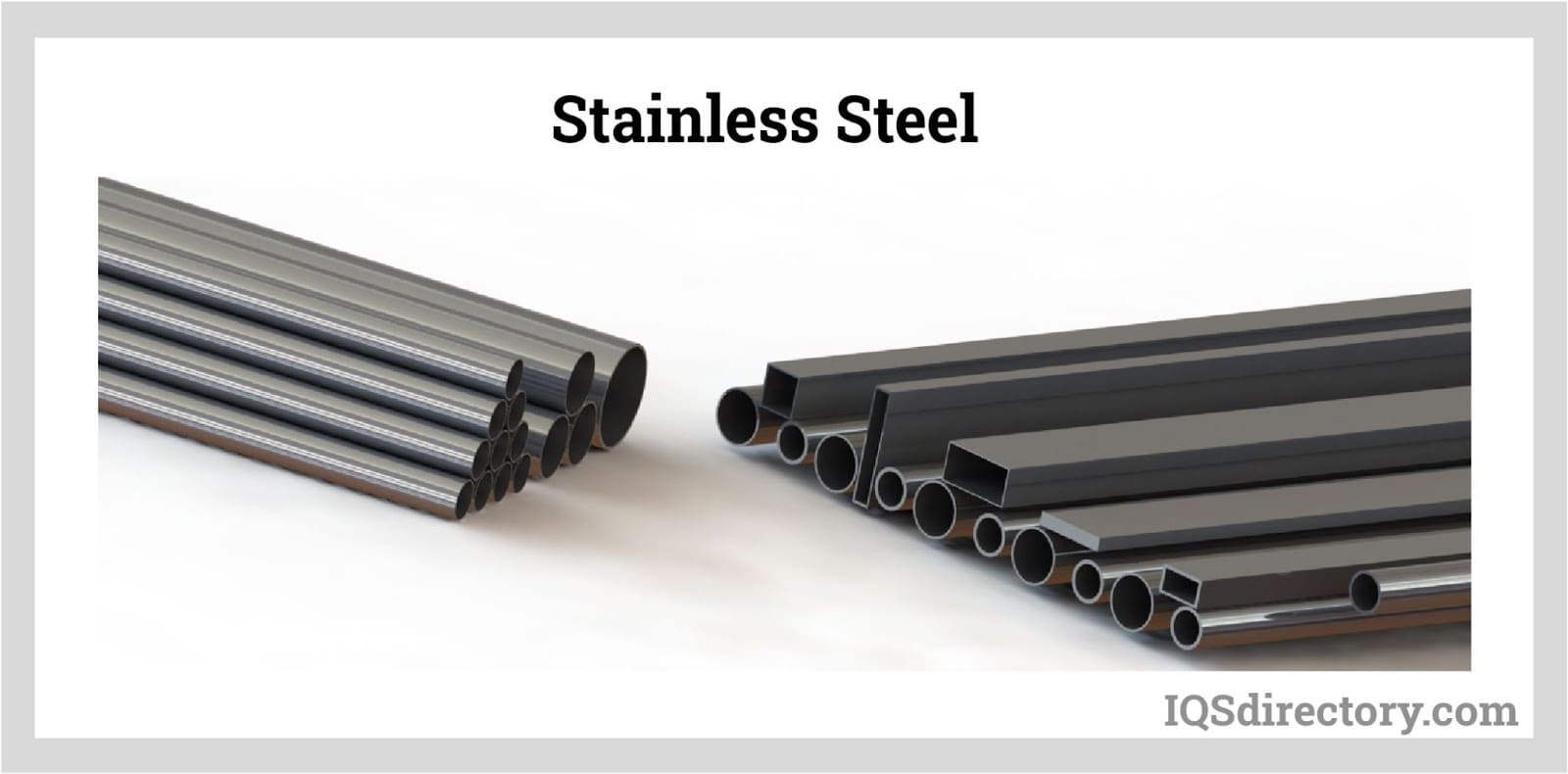
Nickel Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel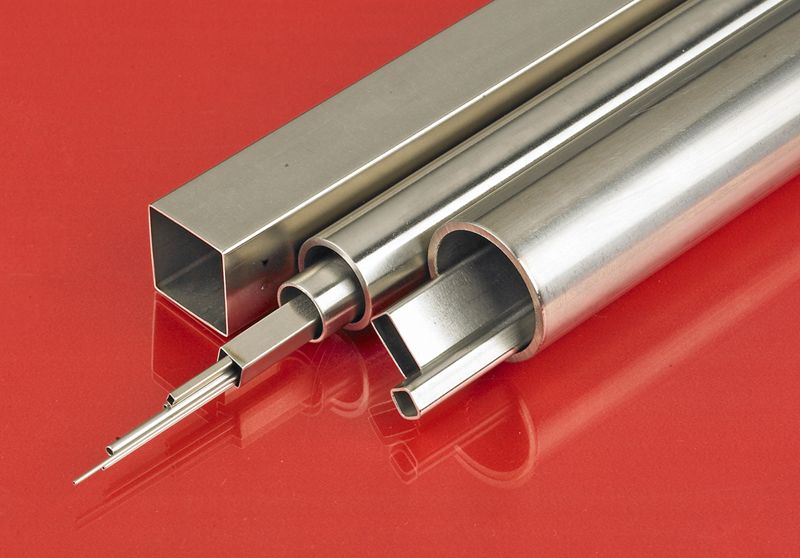 Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers Titanium
Titanium Tungsten
Tungsten Wire Rope
Wire Rope Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services